Anatomy of Fibula Bone: The human body is a remarkable structure, with bones playing a pivotal role in providing support and structure. Among the various bones that make up the human skeleton, the fibula bone, though often overlooked, serves a crucial role in maintaining body stability and aiding in movement. In a recent medical lecture at Tripura’s Santiniketan Medical College, renowned orthopedic surgeon Dr. Pritam Dey delivered an insightful and detailed presentation on the anatomy of the fibula bone. The lecture, aimed at both medical students and professionals, explored the fibula’s anatomy, function, common diseases associated with it, and treatment methods.
The Anatomy of the Fibula
The fibula is a long, thin bone located on the outer side of the lower leg, running parallel to the tibia, which is the primary weight-bearing bone. Dr. Pritam Dey began his lecture by emphasizing the fibula’s role in supporting the tibia while facilitating leg movements. The fibula is not a primary weight-bearing bone; instead, it functions to stabilize and support the tibia, which carries the bulk of the body’s weight during walking, running, and standing.
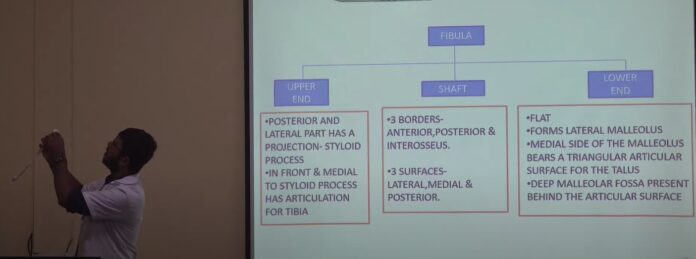
Dr. Dey provided a detailed analysis of the fibula’s structure, starting with its position in the lower leg. The fibula extends from the knee joint to the ankle joint, and its upper end is called the fibular head, where it forms a joint with the tibia. This joint is known as the syndesmosis, a fibrous joint that provides minimal movement but ensures stability.
The fibula is divided into three main parts:
- The Head: Located at the upper end, it forms a joint with the tibia, known as the proximal syndesmosis.
- The Shaft: The long, thin section of the fibula that runs parallel to the tibia.
- The Lateral Malleolus: The bony prominence on the outside of the ankle, which can easily be felt through the skin.
Despite its slender form, the fibula plays a key role in stabilizing the lower leg, particularly during dynamic movements like running or jumping.
The Function of the Fibula
Dr. Dey elaborated on the fibula’s critical role in lower limb function, emphasizing that while it is not directly involved in weight-bearing, it contributes significantly to leg movement and stability. One of the fibula’s most essential functions is as an anchor for several muscles and ligaments in the leg.
The muscles that attach to the fibula, such as the peroneus longus and peroneus brevis, play a vital role in controlling foot movements, especially in tasks like walking, running, and balancing. These muscles help in plantarflexion (pointing the toes downward) and eversion (turning the sole of the foot outward), which are essential for various activities.
Moreover, the fibula serves as a stabilizer for the ankle joint, assisting in maintaining balance and coordination. It works in conjunction with the tibia to provide a smooth and coordinated movement of the lower leg, which is crucial for mobility and proper posture.
Common Diseases and Injuries of the Fibula
Dr. Dey discussed several diseases and injuries associated with the fibula bone, noting that fractures are the most common type of injury. He explained how fibula fractures can occur due to trauma, such as falls, accidents, or sports injuries. In such cases, the fibula may break, typically resulting in swelling, pain, and difficulty in walking.
- Fibula Fractures: These fractures are often categorized into two types:
- Spiral fractures: Occur due to rotational forces, often seen in sports or accidents.
- Oblique fractures: Caused by a direct blow to the bone, typically in accidents or falls.
Fractures of the fibula are often treated with immobilization through casting, though severe fractures may require surgical intervention to align the bone fragments properly.
- Stress Fractures: Repetitive stress on the fibula, particularly from activities like running or jumping, can lead to stress fractures. These fractures are common among athletes and can be challenging to detect, as they are often small and subtle.
- Tendonitis: The fibula also serves as an attachment point for several tendons. When these tendons become inflamed, it can result in a condition called tendonitis. This condition often causes pain and swelling along the outer side of the lower leg, making movement difficult.
- Compartment Syndrome: This is a rare but serious condition that can affect the muscles surrounding the fibula. It occurs when pressure builds up within the muscle compartments, potentially leading to muscle and nerve damage. It is typically a result of trauma and requires immediate medical attention.
- Congenital Conditions: Dr. Dey also highlighted congenital deformities such as fibula hemimelia, where a portion or the entire fibula is absent at birth. This can lead to limb-length discrepancies and may require surgical intervention to address mobility issues.
Treatment and Management of Fibula Injuries
When treating fibula fractures, Dr. Dey stressed the importance of accurate diagnosis and timely intervention. In cases of mild fractures or stress fractures, non-surgical methods like rest, ice, compression, and elevation (R.I.C.E) are commonly recommended. The use of casts or braces helps immobilize the leg and allows the bone to heal in a proper alignment.
In more severe cases, where the fracture is displaced or involves other complications, surgical intervention may be required. Dr. Dey explained that surgeons might use pins, plates, or screws to fix the bone and ensure that it heals in the correct position. Physiotherapy also plays a crucial role in rehabilitation, helping the patient regain strength and mobility after the injury heals.
For conditions like tendonitis or compartment syndrome, non-invasive treatments such as anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and rest are recommended. However, in extreme cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to release the pressure or repair damaged tendons.
Importance of Fibula in Overall Leg Health
Dr. Dey concluded his lecture by reiterating the vital role the fibula plays in maintaining the overall health and functionality of the leg. Although it is not as prominent as the tibia, the fibula is crucial for ensuring the proper movement and stability of the lower limb. Without the fibula’s structural integrity, activities like walking, running, and jumping would be much more difficult and less efficient.
Understanding the anatomy and functions of the fibula bone is essential for medical professionals, particularly orthopedic surgeons and physiotherapists, who treat patients with leg injuries. The lecture provided valuable insights into the fibula’s importance, its potential health issues, and the best practices for managing those issues.
The lecture by Dr. Pritam Dey at Santiniketan Medical College was a significant step in raising awareness about the fibula bone’s role in the human body. By providing a comprehensive understanding of its anatomy, function, common injuries, and treatment strategies, Dr. Dey contributed immensely to the knowledge base of medical students and healthcare professionals. This lecture not only enriched their understanding but also emphasized the importance of considering the fibula in the diagnosis and treatment of lower leg injuries.







[…] READ MORE: Fibula Bone Anatomy: A Comprehensive Guide – Medical Lecture by Dr. Pritam Dey at Tripura Santinik… […]